Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Zoology
EXTERNAL CHARACTERS OF HERDMANIA
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Friday, 07 July 2017 13:43 UTC
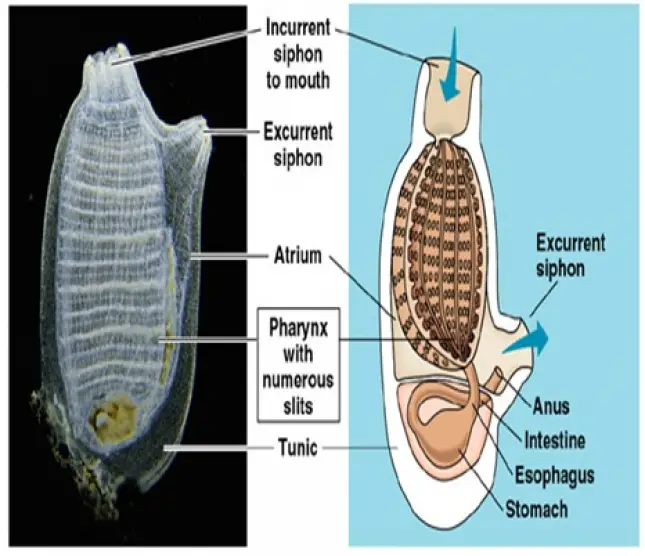
Herdmania is a simple ascidian, In Indian ocean this genus is represented by 4 species.
1. Herdmania pallida 2. H. ennurensis 3. H. mauritiana 4. H. ceylonica
Herdmania belongs to,
- Phylum: Chordata
- Sub-phylum: Urochordata
- Class: Ascidiacea
- Order: Pleurogona
Herdmania is a marine and sedentary animal. It is fixed to rocky substratum by a flat base. When it is disturbed, it suddenly contracts its body, and emits inner contents with force through its apertures. Hence it is called Sea squirt.
External Features:
It is potato like in shape. It is pink in colour. On the free side, body shows two projections, the brançhial and atrial siphons. The branchial siphon is short. The branchial siphon shows a branchial aperture or the mouth. The atrial siphon is longer. It bears the atrial aperture. Both the openings are bounded by four lips.
Herdmania - External Characters:
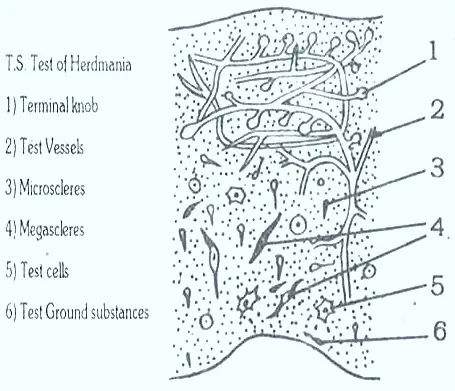
Test of Herdmania:The body of this animal is covered and protected by test. It is a thick, leathery covering of the body. It is secreted by the epidermis of the body wall. It has matrix, corpuscles, fibrils, blood vessels and spicules.
The matrix is composed of tunicin, which is cellulose. The cells in the test are of six types, large eosinophilous cells, amoeboid cells, small eosinophilous cells, vacuolated cells, receptor cells and nerve cells.
Fine fibrils present in the matrix. In the test blood vessels are present. In the test the spicules are calcareous spicules. They are microscleres, and megascleres.
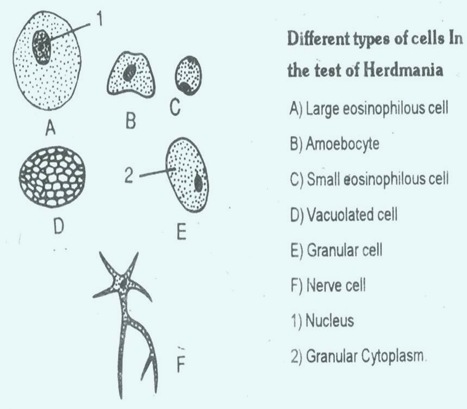
The test protects the body. Anchors the animals to substratum. Its spicules form a supporting frame work.
Herdmania Body Wall:
The body-wall of Herdmania is called Mantle. It is thick, and muscular in the antero-dorsal region of the body. It is thin, non-muscular and transparent in the postero ventral region. It shows epidermis, mesenchyme, and inner epidermis.
1. Epidermis: It Is single layer of cells. It covers the bronchial and atrial apertures and siphons. The epidermis is interrupted at places where spicules and blood-vessels pass from the mantle into the test.
2. Mesenchyme: It develops from the mesoderm. It has connective tissue containing blood-sinuses, muscle-fibers, nerve fibers and cells. The muscle fibers are long and flat. They contain large nuclei.
3. Inner Epidermis: It is single layer of flat cells. It forms the lining of the atrial cavity.
- The body-wall protects visceral organs.
- The outer epidermis secretes the test.
- The musculature brings contraction of the body and the siphons.
Herdmania Atrium:
In Herdmania coelome is not developed. Atrium is a spacious ectoderm lined cavity. it is covered by the mantle A part of the atrium surrounds the pharynx. The stigmata of the pharynx open into this cavity. Part of the atrium is dorsal to the pharynx. It is very wide and is called cloaca. The rectum and gonoducts open into this. The cloaca opens to the exterior through atrial siphon and trial aperture. The atrial siphon shows a ring of processes called atrial tentacles at its base.
End of the article