Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus

In long-standing Diabetes Mellitus (DM) of both types, a wide variety of lesions develop in many organs, which are important causes of morbidity and mortality.
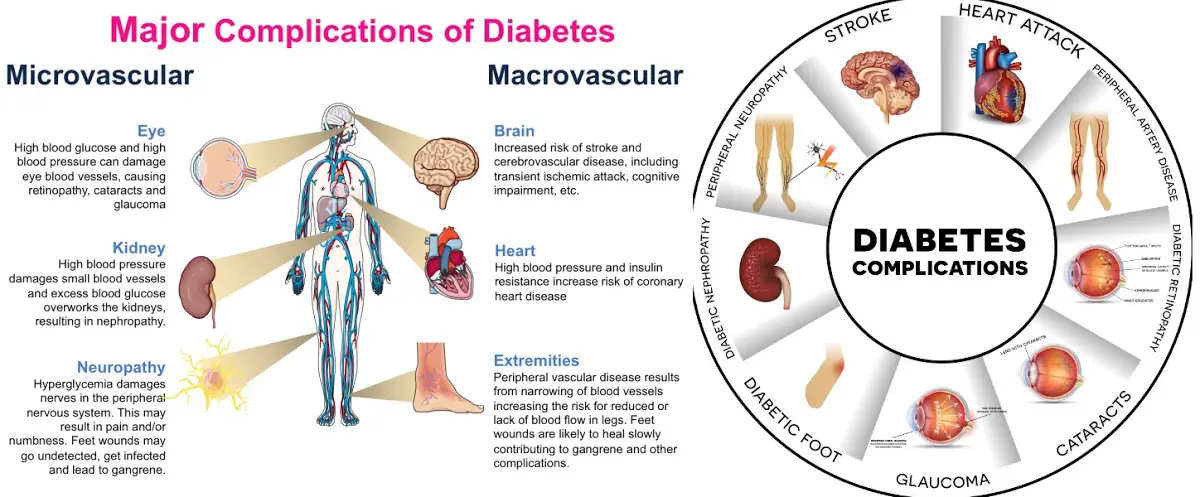
Macroangiopathy (Macrovascular disease): In Diabetes Mellitus (DM), atherosclerosis of aorta and of medium size arteries (like coronary, cerebral, and peripheral) occurs earlier in life and is more extensive than in non-diabetic patients. It can cause myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, and gangrene of lower extremities. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is related to hyperinsulinemia with peripheral insulin resistance and dyslipidemia (raised triglycerides, low high-density lipoprotein or HDL, and raised low-density lipoprotein or LDL).
Microangiopathy (Microvascular disease): Microangiopathy is due to poor diabetes control (Table 1193.1). Microangiopathy (thickening of walls of small blood vessels with narrowing of lumina) is common in kidneys (leading to renal insufficiency), retina (visual impairment), and peripheral nerves (sensory, motor or autonomic neuropathy).
|
Infections: Diabetic patients are susceptible to infections of the skin, respiratory tract (pneumonia, tuberculosis), and kidneys (pyelonephritis).
Average life expectancy of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) patients is reduced. Usual causes of death in Diabetes Mellitus (DM) include myocardial infarction, stroke, renal failure, infections, and ketoacidotic or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic coma.
- Comment
- Posted by Dayyal Dg.